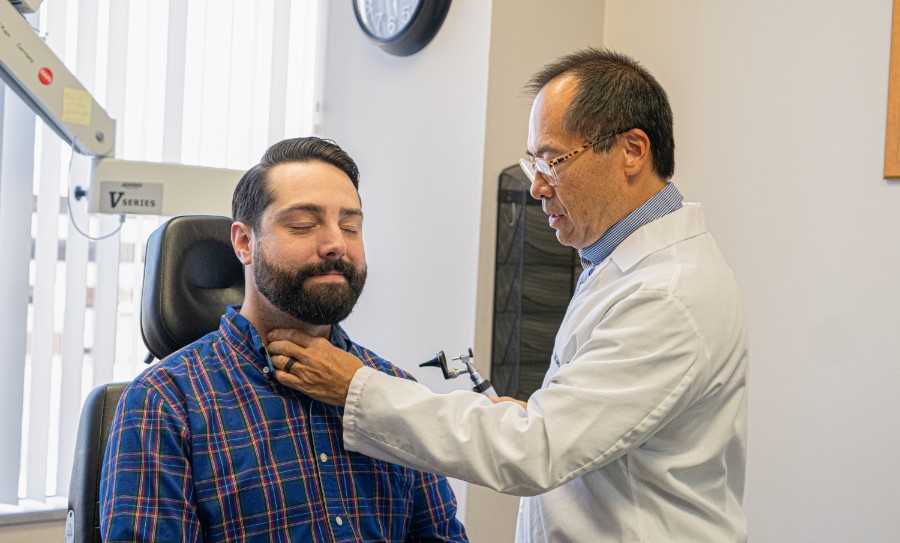
Living with a voice disorder can be hard. Your communication style—the one thing you use to express yourself and connect with others—can be impaired or disrupted in an overwhelming way, affecting your emotional well-being, self-confidence, and ability to take part in the activities you enjoy. Fortunately, voice treatment and therapy are available to help manage symptoms and promote better vocal health outcomes.
With the right guidance from knowledgeable professionals and interventions tailored specifically for you, it’s possible to feel more confident about your speaking abilities again. The Voice and Swallowing Center, a subdivision of ENT & Allergy Associates, specializes in voice disorders and can diagnose and treat a variety of conditions.
A Bit About Voice Therapy
Voice therapy is a crucial tool in treating voice disorders and helping individuals recover their vocal abilities. This therapy effectively targets specific vocal behaviors and promotes the healing of the vocal cords to restore vocal strength. Additionally, voice therapy can be used as a preventative measure to avoid voice disorders altogether.
In cases of transgender individuals, gender-affirming voice therapy offers a powerful avenue for vocal transformation and alignment with personal identity. With the guidance of a professional, voice therapy can significantly improve your vocal performance, offering newfound confidence and clarity in everyday life.
Traditional voice therapy consists of two primary avenues: Vocal Hygiene and Voice Therapy. Vocal hygiene is a daily regimen to achieve and maintain a healthy voice. Vocal hygiene includes maintaining adequate hydration (6-8 glasses of water per day), minimizing exposure to noxious chemicals, not smoking cigarettes, and avoiding excessive shouting, screaming, or other loud voice use. Voice therapy is a behavioral intervention technique that makes use of vocal exercises, speaker awareness, and proper postures and alignment when using the voice.
Learn More – Schedule Your Appointment Today
Voice treatment and therapy can be a great resource to improve vocal performance and address voice disorders. And with the experienced health professionals, you know that you are in good hands. What's more, there is no need to fear complications, as professional treatments are tailored to each individual’s specific needs.
So if you've been feeling like something has been holding your performance or career back, consider visiting a Voice and Swallowing Center. With the right diagnosis and care plan you will quickly be able to take control of your progress. This should be followed by increased confidence and an improved ability to deliver great performances!
Patient Stories
-
"Very personalized service from staff to Doctor especially Dr. Alaxander S."
- Shabbir A. -
"Really listens to your concerns. Super thorough & knowledgeable."
- M.L. -
"Beyond expectations, I felt comfortable, at ease, and left without any questions unanswered, knowing that his approach to my situation was working and the right course of treatment."
- R.E.
Less Sick Days, More Living

